EventBridge
Introduction
Section titled “Introduction”EventBridge provides a centralized mechanism to discover and communicate events across various AWS services and applications. EventBridge allows you to register, track, and resolve events, which indicates a change in the environment and then applies a rule to route the event to a target. EventBridge rules are tied to an Event Bus to manage event-driven workflows. You can use either identity-based or resource-based policies to control access to EventBridge resources, where the former can be attached to IAM users, groups, and roles, and the latter can be attached to specific AWS resources.
LocalStack allows you to use the EventBridge APIs in your local environment to create rules that route events to a target. The supported APIs are available on our API Coverage section, which provides information on the extent of EventBridge’s integration with LocalStack. For information on EventBridge Pipes, please refer to the EventBridge Pipes documentation.
Getting Started
Section titled “Getting Started”This guide is designed for users new to EventBridge and assumes basic knowledge of the AWS CLI and our awslocal wrapper script.
Start your LocalStack container using your preferred method. We will demonstrate creating an EventBridge rule to run a Lambda function when a custom event is published to an event bus.
Create an EventBridge Bus
Section titled “Create an EventBridge Bus”First, create a custom EventBridge bus using the CreateEventBus API:
awslocal events create-event-bus \ --name my-custom-busWhile you can always use the default event bridge bus automatically available and configured for your account in any region, custom event buses are much more commonly used in practice and provide better organization for your events.
Create a Lambda Function
Section titled “Create a Lambda Function”To create a new Lambda function, create a new file called index.js with the following code:
'use strict';
exports.handler = (event, context, callback) => { console.log('LogEventBridgeEvent'); console.log('Received event:', JSON.stringify(event, null, 2)); callback(null, 'Finished');};Run the following command to create a new Lambda function using the CreateFunction API:
zip function.zip index.js
awslocal lambda create-function \ --function-name events-example \ --runtime nodejs16.x \ --zip-file fileb://function.zip \ --handler index.handler \ --role arn:aws:iam::000000000000:role/cool-stacklifterThe output will consist of the FunctionArn, which you will need to add the Lambda function to the EventBridge target.
Create an EventBridge Rule
Section titled “Create an EventBridge Rule”Run the following command to create a new EventBridge rule using the PutRule API:
awslocal events put-rule \ --name my-custom-rule \ --event-bus-name my-custom-bus \ --event-pattern '{"source":["my-source"],"detail-type":["my-detail-type"]}' \ --state ENABLEDIn the above command, we have specified an event pattern that will match events with:
sourcefield equal tomy-sourcedetail-typefield equal tomy-detail-type
This rule will trigger whenever an event matching this pattern is published to the custom event bus.
Next, grant the EventBridge service principal (events.amazonaws.com) permission to run the rule, using the AddPermission API:
awslocal lambda add-permission \ --function-name events-example \ --statement-id my-custom-event \ --action 'lambda:InvokeFunction' \ --principal events.amazonaws.com \ --source-arn arn:aws:events:us-east-1:000000000000:rule/my-custom-bus/my-custom-ruleAdd the Lambda Function as a Target
Section titled “Add the Lambda Function as a Target”Create a file named targets.json with the following content:
[ { "Id": "1", "Arn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:000000000000:function:events-example" }]Finally, add the Lambda function as a target to the EventBridge rule using the PutTargets API:
awslocal events put-targets \ --rule my-custom-rule \ --event-bus-name my-custom-bus \ --targets file://targets.jsonSend an Event to Trigger the Lambda
Section titled “Send an Event to Trigger the Lambda”Now, send an event that matches the rule pattern to trigger the Lambda function using the PutEvents API:
awslocal events put-events \ --entries '[{"Source": "my-source", "DetailType": "my-detail-type", "Detail": "{\"key\": \"value\"}", "EventBusName": "my-custom-bus"}]'This event will match the pattern we defined in the rule and should trigger the Lambda function immediately.
Verify the Lambda invocation
Section titled “Verify the Lambda invocation”You can verify the Lambda invocation by checking the CloudWatch logs.
Run the following command to list the CloudWatch log groups:
awslocal logs describe-log-groupsThe output will contain the log group name, which you can use to list the log streams:
awslocal logs describe-log-streams \ --log-group-name /aws/lambda/events-exampleAlternatively, you can fetch LocalStack logs to verify the Lambda invocation:
localstack logs...2023-07-17T09:37:52.028 INFO --- [ asgi_gw_0] localstack.request.aws : AWS lambda.Invoke => 2022023-07-17T09:37:52.106 INFO --- [ asgi_gw_0] localstack.request.http : POST /_localstack_lambda/97e08ac50c18930f131d9dd9744b8df4/invocations/ecb744d0-b3f2-400f-9e49-c85cf12b1e00/logs => 2022023-07-17T09:37:52.114 INFO --- [ asgi_gw_0] localstack.request.http : POST /_localstack_lambda/97e08ac50c18930f131d9dd9744b8df4/invocations/ecb744d0-b3f2-400f-9e49-c85cf12b1e00/response => 202...Supported target types
Section titled “Supported target types”At this time LocalStack supports the following target types for EventBridge rules:
- Lambda function
- SNS Topic
- SQS queue
- StepFunctions StateMachine
- Firehose
- Event bus
- API destination
- Kinesis
- CloudWatch log group
- API Gateway
Resource Browser
Section titled “Resource Browser”The LocalStack Web Application provides a Resource Browser for managing EventBridge Buses. You can access the Resource Browser by opening the LocalStack Web Application in your browser, navigating to the Resources section, and then clicking on EventBridge under the App Integration section.
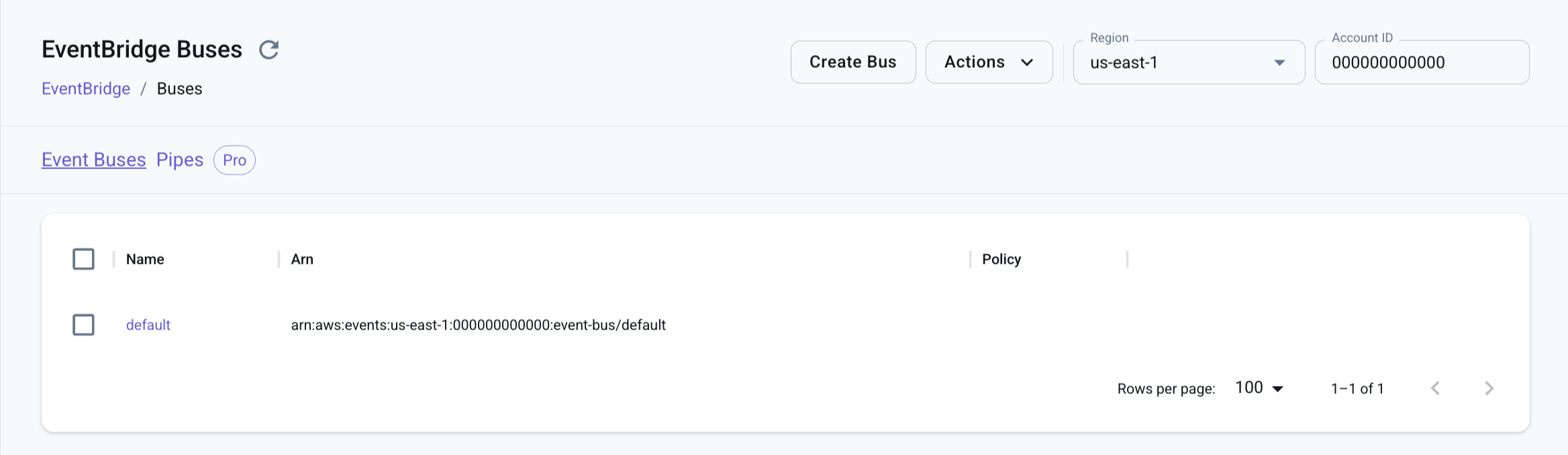
The Resource Browser allows you to perform the following actions:
- View the Event Buses: You can view the list of EventBridge Buses running locally, alongside their Amazon Resource Names (ARNs) and Policies.
- Create Event Rule: You can create a new Event Rule by specifying Name, Description, Event Pattern, Schedule Expressions, State, Role ARN, and Tags.
- Trigger Event: You can trigger an Event by specifying the Entries and Endpoint Id. While creating an Entry, you must specify Source, Event Bus Name, Detail, Resources, Detail Type, and Trace Header.
- Remove Selected: You can remove the selected EventBridge Bus.
API Coverage
Section titled “API Coverage”| Operation ▲ | Implemented | Image |
|---|